NCATS Enables IND Clearances and Drug Approvals
Our labs play a critical, hands-on role in getting new therapies to patients by partnering to discover and develop drugs for rare diseases and other unmet medical needs.
An Investigational New Drug (IND) application is a key milestone in drug discovery—it marks the first step toward initiating first-in-human trials for a new medicine. IND applications allow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to review a drug’s quality and safety. FDA clearance of an IND is a critical turning point as it brings a drug product closer to reaching patients in need.
When a drug advances successfully through all phases of clinical trials, the trial sponsor can submit a New Drug Application (NDA). An NDA is a request to bring a new drug to market to the FDA. FDA approval of an NDA means that a new medicine is now available to treat patients.
NCATS plays a pivotal role in progressing new therapeutics to market, directly benefiting patients. We partner with external researchers to help bridge the gap between the preclinical and clinical stages of therapeutic development. We do this by advancing promising medicinal agents through late-stage preclinical development and IND-enabling studies. Our scientists also develop small molecules that drug companies can license and further develop for clinical trials.
To date, 56 IND clearances and 4 NDA approvals have resulted from research conducted at NCATS as part of our Intramural Research Program.
Explore NCATS-enabled IND clearances and NDA approvals.
60
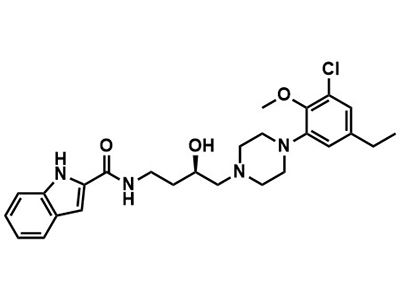
R-VK4-116
Small Molecule
R-VK4-116 is intended as an oral treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) and as a co-treatment to lower the dose of prescription opioids and reduce risk of dependence.
R-VK4-116
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Opioid Use Disorder
Target:
Dopamine receptor antagonist (D3R)
Indication & Usage:
R-VK4-116 is intended as an oral treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) and as a co-treatment to lower the dose of prescription opioids and reduce risk of dependence.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2025 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
R-VK4-116 is an oral drug under investigation for the treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD), a public health crisis affecting more than 16 million people worldwide. R-VK4-116 is a small molecule antagonist of the dopamine receptor pathway (D3R), a novel therapeutic target for stopping addictive behaviors. In animal models, pre-treatment with R-VK4-116 dose-dependently reduced drug-seeking behaviors and withdrawal symptoms, effects that are critical for therapeutic use.

Opioid Use Disorder
Dopamine receptor antagonist (D3R)
R-VK4-116 is intended as an oral treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) and as a co-treatment to lower the dose of prescription opioids and reduce risk of dependence.
2025 (FDA)
R-VK4-116 is an oral drug under investigation for the treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD), a public health crisis affecting more than 16 million people worldwide. R-VK4-116 is a small molecule antagonist of the dopamine receptor pathway (D3R), a novel therapeutic target for stopping addictive behaviors. In animal models, pre-treatment with R-VK4-116 dose-dependently reduced drug-seeking behaviors and withdrawal symptoms, effects that are critical for therapeutic use.
59

Sargmalin® (Inhaled GM-CSF)
Protein
Sargmalin® is an inhaled formulation of GM-CSF that is approved for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
Sargmalin® (Inhaled GM-CSF)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Cincinnati Children's Hospital, Partner Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Cincinnati Children's Hospital, Partner Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP)
Target:
Alveolar macrophages
Indication & Usage:
Sargmalin® is an inhaled formulation of GM-CSF that is approved for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2024 (PMDA (Japan))
Public Health Impact:
Nebulized granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a treatment for autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis by stimulating the patient’s immune cells. This lessens the need for invasive whole-lung lavage procedures that require general anesthesia and hospitalization. The inhaled formulation lets patients self-administer the therapy at home.

Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP)
Alveolar macrophages
Sargmalin® is an inhaled formulation of GM-CSF that is approved for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
2024 (PMDA (Japan))
Nebulized granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a treatment for autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis by stimulating the patient’s immune cells. This lessens the need for invasive whole-lung lavage procedures that require general anesthesia and hospitalization. The inhaled formulation lets patients self-administer the therapy at home.
58

GS-441524
Small Molecule
GS-441524 is intended as an oral treatment for COVID-19 in patients of all ages.
GS-441524
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
N/A
Therapeutic Area:
Infectious Disease
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
N/A
Therapeutic Area:
Infectious Disease
Disease:
COVID-19
Target:
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase pathway
Indication & Usage:
GS-441524 is intended as an oral treatment for COVID-19 in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2024 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
GS-441524, an antiviral candidate first developed by Gilead Sciences, is being developed as a broad-spectrum antiviral oral treatment for COVID-19 and other pandemic-threat viruses. GS-441524 is a metabolite of remdesivir, an antiviral drug that is used against SARS-CoV-2 infection but can only be administered intravenously in a health care setting, limiting patient access.

COVID-19
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase pathway
GS-441524 is intended as an oral treatment for COVID-19 in patients of all ages.
2024 (FDA)
GS-441524, an antiviral candidate first developed by Gilead Sciences, is being developed as a broad-spectrum antiviral oral treatment for COVID-19 and other pandemic-threat viruses. GS-441524 is a metabolite of remdesivir, an antiviral drug that is used against SARS-CoV-2 infection but can only be administered intravenously in a health care setting, limiting patient access.
57

KME-0584
Small Molecule
KME-0584 is intended for use as a treatment for relapsed/refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high-risk (HR) myelodysplastic syndrome.
KME-0584
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Kurome Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Blood Cancers
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Kurome Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Blood Cancers
Disease:
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) / Myleodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
Target:
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)
Indication & Usage:
KME-0584 is intended for use as a treatment for relapsed/refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high-risk (HR) myelodysplastic syndrome.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2023 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
KME-0584 is a dual inhibitor of the FLT3 and IRAK kinases developed to treat myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, blood cancers typically treated with chemotherapy that fails to produce durable remission.

Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) / Myleodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)
KME-0584 is intended for use as a treatment for relapsed/refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high-risk (HR) myelodysplastic syndrome.
2023 (FDA)
KME-0584 is a dual inhibitor of the FLT3 and IRAK kinases developed to treat myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, blood cancers typically treated with chemotherapy that fails to produce durable remission.
56

PTH-IA
Protein
PTH-IA is intended for treating Jansen’s metaphyseal chondrodysplasia in patients of all ages.
PTH-IA
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Jansen’s Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia (JMC)
Target:
Mutated parathyroid hormone receptor (PTHR1)
Indication & Usage:
PTH-IA is intended for treating Jansen’s metaphyseal chondrodysplasia in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2023 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Parathyroid Hormone-Inverse Agonist (PTH-IA) is a peptide drug that reduces the overactivity of mutant PTH receptors, improving the bone and mineral defects of Jansen’s metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, an ultrarare bone disease for which there is no effective treatment or cure.

Jansen’s Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia (JMC)
Mutated parathyroid hormone receptor (PTHR1)
PTH-IA is intended for treating Jansen’s metaphyseal chondrodysplasia in patients of all ages.
2023 (FDA)
Parathyroid Hormone-Inverse Agonist (PTH-IA) is a peptide drug that reduces the overactivity of mutant PTH receptors, improving the bone and mineral defects of Jansen’s metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, an ultrarare bone disease for which there is no effective treatment or cure.
55

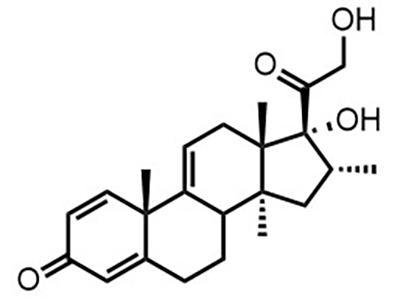
Agamree® (Vamorolone)
Small Molecule
Agamree® is a corticosteroid approved for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
Agamree® (Vamorolone)

 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
ReveraGen
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
ReveraGen
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Target:
Glucocorticoid receptor
Indication & Usage:
Agamree® is a corticosteroid approved for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2023 (FDA, EMA (EU); MHRA (UK))
Public Health Impact:
Agamree® is a dissociative anti-inflammatory steroid (corticosteroid) that decouples positive therapeutic effects from some of the negative side effects linked to traditional corticosteroid use. It is currently approved for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a rare genetic childhood disease that slowly causes weakness and loss of muscle function.


Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Glucocorticoid receptor
Agamree® is a corticosteroid approved for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
2023 (FDA, EMA (EU); MHRA (UK))
Agamree® is a dissociative anti-inflammatory steroid (corticosteroid) that decouples positive therapeutic effects from some of the negative side effects linked to traditional corticosteroid use. It is currently approved for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a rare genetic childhood disease that slowly causes weakness and loss of muscle function.
54

Kebilidi™ (AGIL-AADC)
Gene Therapy
Kebilidi is a gene therapy approved to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
Kebilidi™ (AGIL-AADC)
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Agilis Biotherapeutics (prior to acquisition by PTC Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Agilis Biotherapeutics (prior to acquisition by PTC Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Target:
Delivers the functional DDC gene directly into the putamen
Indication & Usage:
Kebilidi is a gene therapy approved to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2024 (FDA); 2022 (EMA (EU); MHRA (UK) as UPSTAZA™)
Public Health Impact:
Kebilidi™ is a one-time gene replacement therapy developed to treat L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. The deficiency is a rare inherited disease that affects the central nervous system, causing developmental delays, weak muscle tone, and an inability to control movement of the limbs. Kebilidi™ increases dopamine and serotonin production, improving motor and cognitive functions and reducing severe symptoms.

Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Delivers the functional DDC gene directly into the putamen
Kebilidi is a gene therapy approved to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
2024 (FDA); 2022 (EMA (EU); MHRA (UK) as UPSTAZA™)
Kebilidi™ is a one-time gene replacement therapy developed to treat L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. The deficiency is a rare inherited disease that affects the central nervous system, causing developmental delays, weak muscle tone, and an inability to control movement of the limbs. Kebilidi™ increases dopamine and serotonin production, improving motor and cognitive functions and reducing severe symptoms.
53

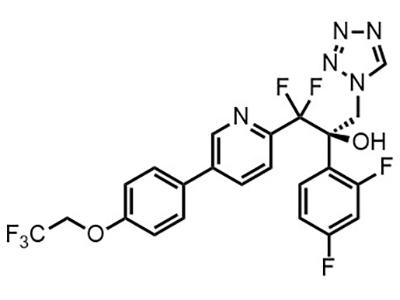
Vivjoa® (Oteseconazole)
Small Molecule
Vivjoa® (Oteseconazole) is an antifungal medication approved for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
Vivjoa® (Oteseconazole)

 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Target:
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Indication & Usage:
Vivjoa is an antifungal medication approved for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2022 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Vivjoa® is an oral antifungal medication that treats chronic yeast infection by inhibiting the growth and spread of fungi. It blocks the cytochrome P450 enzyme 51 in microbes while having a lower affinity for the human variant, helping to decrease off-target toxicity.


Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Vivjoa is an antifungal medication approved for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
2022 (FDA)
Vivjoa® is an oral antifungal medication that treats chronic yeast infection by inhibiting the growth and spread of fungi. It blocks the cytochrome P450 enzyme 51 in microbes while having a lower affinity for the human variant, helping to decrease off-target toxicity.
52

Q-Griffithsin (Q-GRFT)
Protein
Q-GRFT is a nasal spray intended to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals of all ages.
Q-Griffithsin (Q-GRFT)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
University of Lousiville; University of Pittsburgh
Therapeutic Area:
Infectious Disease
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
University of Lousiville; University of Pittsburgh
Therapeutic Area:
Infectious Disease
Disease:
COVID-19
Target:
Glycosylated spike proteins
Indication & Usage:
Q-GRFT is a nasal spray intended to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2021 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Q-Griffithsin (Q-GRFT) is a protein from red algae formulated as a nasal spray that stops the cellular entry of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses, providing a preventive option to prevent COVID-19 infection.

COVID-19
Glycosylated spike proteins
Q-GRFT is a nasal spray intended to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals of all ages.
2021 (FDA)
Q-Griffithsin (Q-GRFT) is a protein from red algae formulated as a nasal spray that stops the cellular entry of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses, providing a preventive option to prevent COVID-19 infection.
51
TPM-001
Drug Vehicle
The timed-release microparticle formulation of paclitaxel (TPM-001) is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer and other peritoneal tumors in adults.
TPM-001
 Modality:
Drug Vehicle
Partner(s):
Optimum Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Modality:
Drug Vehicle
Partner(s):
Optimum Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Pancreatic Cancer
Target:
Anatomical properties of the peritoneal cavity
Indication & Usage:
The timed-release microparticle formulation of paclitaxel (TPM-001) is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer and other peritoneal tumors in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2021 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Tumor-penetrating microparticles (TPMs) are a first-in-class delivery system designed to target, penetrate, and deliver drugs to the superficial and deep layers of abdominal tumors. TPM-001 improves the penetration of paclitaxel into solid tumors, enhancing anticancer efficacy while reducing toxicity and offering a new approach for treating abdominal cancers.

Pancreatic Cancer
Anatomical properties of the peritoneal cavity
The timed-release microparticle formulation of paclitaxel (TPM-001) is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer and other peritoneal tumors in adults.
2021 (FDA)
Tumor-penetrating microparticles (TPMs) are a first-in-class delivery system designed to target, penetrate, and deliver drugs to the superficial and deep layers of abdominal tumors. TPM-001 improves the penetration of paclitaxel into solid tumors, enhancing anticancer efficacy while reducing toxicity and offering a new approach for treating abdominal cancers.
50

iNexin (aCT1)
Protein
iNexin is intended for the treatment of diabetic keratopathy in patients with diabetes.
iNexin (aCT1)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Xequel Bio (formerly FirstString Research)
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Xequel Bio (formerly FirstString Research)
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Diabetic Keratopathy
Target:
Connexin43 (Cx43)
Indication & Usage:
iNexin is intended for the treatment of diabetic keratopathy in patients with diabetes.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2021 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
iNexin Opthalmic Solution (aCT1) is a new treatment for diabetic keratopathy, a common and serious complication of diabetes that affects the cornea and can result in vision loss. iNexin promotes wound closure and corneal re-epithelialization, a vital step in rebuilding the cornea’s imaging properties and protective barrier.

Diabetic Keratopathy
Connexin43 (Cx43)
iNexin is intended for the treatment of diabetic keratopathy in patients with diabetes.
2021 (FDA)
iNexin Opthalmic Solution (aCT1) is a new treatment for diabetic keratopathy, a common and serious complication of diabetes that affects the cornea and can result in vision loss. iNexin promotes wound closure and corneal re-epithelialization, a vital step in rebuilding the cornea’s imaging properties and protective barrier.
49
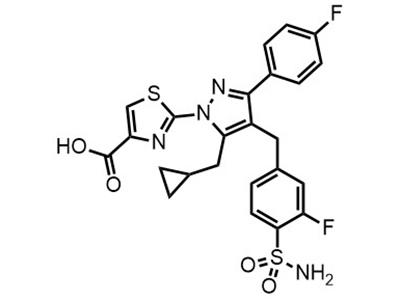
CHK-336
Small Molecule
CHK-336 is intended for use as a treatment for hyperoxalurias in adults.
CHK-336
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Chinook Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Nephrology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Chinook Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Nephrology
Disease:
Primary and Idiopathic Hyperoxaluria
Target:
Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA)
Indication & Usage:
CHK-336 is intended for use as a treatment for hyperoxalurias in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2022 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
CHK-336 is a first-in-class oral small molecule inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase A, a historically intractable drug target. CHK-336 is being designed to treat primary hyperoxalurias (PH) and other kidney stone disorders caused by the overproduction of oxalate. There are limited therapeutic options for PH. CHK-336 is the first liver-targeted drug compound that shows potent, selective inhibition of LDHA, the enzyme responsible for the final step in the synthesis of oxalate in the liver.

Primary and Idiopathic Hyperoxaluria
Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA)
CHK-336 is intended for use as a treatment for hyperoxalurias in adults.
2022 (FDA)
CHK-336 is a first-in-class oral small molecule inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase A, a historically intractable drug target. CHK-336 is being designed to treat primary hyperoxalurias (PH) and other kidney stone disorders caused by the overproduction of oxalate. There are limited therapeutic options for PH. CHK-336 is the first liver-targeted drug compound that shows potent, selective inhibition of LDHA, the enzyme responsible for the final step in the synthesis of oxalate in the liver.
48
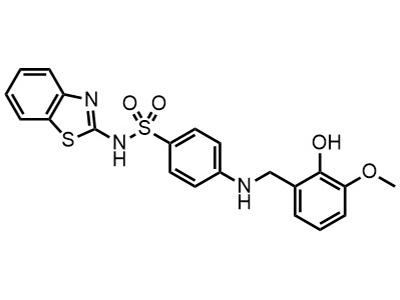
VLX-1005
Small Molecule
VLX-1005 is intended for the treatment or prevention of abnormal blood clots in adults with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
VLX-1005
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Veralox Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Veralox Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
Target:
12-Lipoxygenase (12LOX)
Indication & Usage:
VLX-1005 is intended for the treatment or prevention of abnormal blood clots in adults with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2021 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
VLX-1005 is a first-in-class small molecule clinical candidate in development to treat heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). HIT is an immune complication of heparin therapy and the most serious and frequent drug-induced type of thrombocytopenia. VLX-1005 is an inhibitor of 12-lipoxygenase and has been shown to stop immune-driven platelet activation and thrombosis, making it a potentially lifesaving therapy for patients with HIT.

Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
12-Lipoxygenase (12LOX)
VLX-1005 is intended for the treatment or prevention of abnormal blood clots in adults with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
2021 (FDA)
VLX-1005 is a first-in-class small molecule clinical candidate in development to treat heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). HIT is an immune complication of heparin therapy and the most serious and frequent drug-induced type of thrombocytopenia. VLX-1005 is an inhibitor of 12-lipoxygenase and has been shown to stop immune-driven platelet activation and thrombosis, making it a potentially lifesaving therapy for patients with HIT.
47
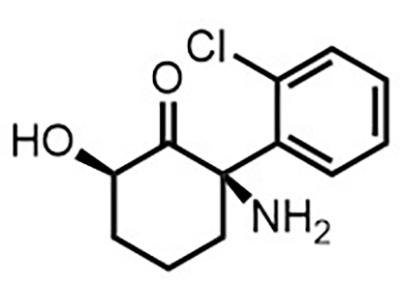
RR-HNK
Small Molecule
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (RR-HNK) is intended for use as a treatment for depression, OCD, and pain in adults.
RR-HNK
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
NIMH
Therapeutic Area:
Mental Health
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
NIMH
Therapeutic Area:
Mental Health
Disease:
Depression, OCD, Pain
Target:
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR)
Indication & Usage:
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (RR-HNK) is intended for use as a treatment for depression, OCD, and pain in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2020 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (RR-HNK), a metabolite of ketamine, is being developed as a new therapy for mental health disorders. Major depressive disorder, including treatment-resistant depression, is one of the most common mental health diseases worldwide. RR-HNK has shown promising antidepressant activity in animal models at doses that do not cause the dissociative or anesthetic effects of ketamine. This removes the unwanted side effects from the therapeutic benefit.

Depression, OCD, Pain
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR)
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (RR-HNK) is intended for use as a treatment for depression, OCD, and pain in adults.
2020 (FDA)
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (RR-HNK), a metabolite of ketamine, is being developed as a new therapy for mental health disorders. Major depressive disorder, including treatment-resistant depression, is one of the most common mental health diseases worldwide. RR-HNK has shown promising antidepressant activity in animal models at doses that do not cause the dissociative or anesthetic effects of ketamine. This removes the unwanted side effects from the therapeutic benefit.
46

Eneboparatide (AZP-3601)
Peptide
Eneboparatide is intended for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism in adults and children.
Eneboparatide (AZP-3601)
 Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital (licensed by AstraZeneca)
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital (licensed by AstraZeneca)
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Hypoparathyroidism
Target:
Parathyroid hormone/Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTH/PTHrP) receptor (PTHR1)
Indication & Usage:
Eneboparatide is intended for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism in adults and children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2020 (EMA (EU); FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Eneboparatide (AZP-3601) is a therapeutic peptide designed to provide stable and sustained elevation of calcium levels in the blood to manage the symptoms of hypoparathyroidism. The drug also reduces urinary calcium excretion and blood phosphorus, preventing progressive decline in kidney function, and it has a short half-life to help maintain bone density. As a result, eneboparatide is an improved treatment for hypoparathyroidism compared to existing therapies.

Hypoparathyroidism
Parathyroid hormone/Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTH/PTHrP) receptor (PTHR1)
Eneboparatide is intended for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism in adults and children.
2020 (EMA (EU); FDA)
Eneboparatide (AZP-3601) is a therapeutic peptide designed to provide stable and sustained elevation of calcium levels in the blood to manage the symptoms of hypoparathyroidism. The drug also reduces urinary calcium excretion and blood phosphorus, preventing progressive decline in kidney function, and it has a short half-life to help maintain bone density. As a result, eneboparatide is an improved treatment for hypoparathyroidism compared to existing therapies.
45
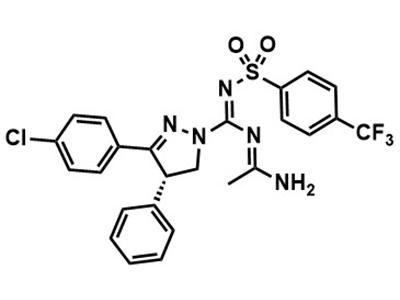
Zevaquenabant (INV-101)
Small Molecule
Zevaquenabant is intended for treating pulmonary fibrosis primarily in adult patients with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.
Zevaquenabant (INV-101)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (HPS) Pulmonary Fibrosis
Target:
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) pathways
Indication & Usage:
Zevaquenabant is intended for treating pulmonary fibrosis primarily in adult patients with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2020 (Health Canada)
Public Health Impact:
Zevaquenabant (INV-101) is a peripherally active cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) inverse agonist made to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). IPF patients typically have a poor prognosis with a median life expectancy of about 3 years beyond initial diagnosis. There is a significant unmet need for effective therapies. Zevaquenabant works by blocking CB1R outside of the brain (“peripheral” CB1R), which reduces lung scarring and inflammation.

Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (HPS) Pulmonary Fibrosis
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) pathways
Zevaquenabant is intended for treating pulmonary fibrosis primarily in adult patients with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.
2020 (Health Canada)
Zevaquenabant (INV-101) is a peripherally active cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) inverse agonist made to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). IPF patients typically have a poor prognosis with a median life expectancy of about 3 years beyond initial diagnosis. There is a significant unmet need for effective therapies. Zevaquenabant works by blocking CB1R outside of the brain (“peripheral” CB1R), which reduces lung scarring and inflammation.
44

TTHX1114 (NM141)
Protein
TTHX1114 is intended to treat Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy in patients aged 18 and older.
TTHX1114 (NM141)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Trefoil Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Trefoil Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Fuchs' Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD)
Target:
Fibroblast growth factor 1
Indication & Usage:
TTHX1114 is intended to treat Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy in patients aged 18 and older.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2020 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
TTHX1114 is an engineered variant of fibroblast growth factor-1, a naturally occurring molecule that triggers corneal endothelial and epithelial cell proliferation and protects from stress and injury. The drug aims to improve vision by halting the loss of and potentially regenerating corneal endothelial cells in patients with Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy.

Fuchs' Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD)
Fibroblast growth factor 1
TTHX1114 is intended to treat Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy in patients aged 18 and older.
2020 (FDA)
TTHX1114 is an engineered variant of fibroblast growth factor-1, a naturally occurring molecule that triggers corneal endothelial and epithelial cell proliferation and protects from stress and injury. The drug aims to improve vision by halting the loss of and potentially regenerating corneal endothelial cells in patients with Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy.
43
Metarrestin (ML-246)
Small Molecule
Metarrestin is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer in adults and children ages 12 to 17.
Metarrestin (ML-246)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Cancer Institute (NCI); Oncala Bio
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Cancer Institute (NCI); Oncala Bio
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Pancreatic Cancer
Target:
Perinucleolar compartment (PNC)
Indication & Usage:
Metarrestin is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer in adults and children ages 12 to 17.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Metarrestin is a first-in-class small molecule inhibitor that represents a new class of cancer therapeutics. These therapeutics are designed to block the metastatic process by targeting the perinucleolar compartment (PNC), a subdomain of the nucleus. The PNC is linked to cancer progression and metastatic capacity. Metarrestin has been shown to reduce metastatic burden in pancreatic cancer, potentially improving patient survival and quality of life.

Pancreatic Cancer
Perinucleolar compartment (PNC)
Metarrestin is intended for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer in adults and children ages 12 to 17.
2019 (FDA)
Metarrestin is a first-in-class small molecule inhibitor that represents a new class of cancer therapeutics. These therapeutics are designed to block the metastatic process by targeting the perinucleolar compartment (PNC), a subdomain of the nucleus. The PNC is linked to cancer progression and metastatic capacity. Metarrestin has been shown to reduce metastatic burden in pancreatic cancer, potentially improving patient survival and quality of life.
42
Zalunfiban (RUC-4)
Small Molecule
Zalunfiban is intended for the pre-hospital treatment of ST segment-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) in adults.
Zalunfiban (RUC-4)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Rockefeller University; CeleCor Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Rockefeller University; CeleCor Therapeutics
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Target:
αIIbβ3 integrin
Indication & Usage:
Zalunfiban is intended for the pre-hospital treatment of ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Zalunfiban, a novel subcutaneously administered glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor, reduces early mortality and the onset of congestive heart failure in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction by preventing platelet aggregation and cardiac damage. Zalunfiban is administered to patients in the prehospital setting and has been shown to achieve rapid, high-grade platelet inhibition.

Myocardial Infarction (MI)
αIIbβ3 integrin
Zalunfiban is intended for the pre-hospital treatment of ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in adults.
2019 (FDA)
Zalunfiban, a novel subcutaneously administered glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor, reduces early mortality and the onset of congestive heart failure in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction by preventing platelet aggregation and cardiac damage. Zalunfiban is administered to patients in the prehospital setting and has been shown to achieve rapid, high-grade platelet inhibition.
41

HBN-1
Small Molecule
HBN-1 is intended for inducing regulated therapeutic hypothermia in adults resuscitated from cardiac arrest.
HBN-1
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Target:
Hypothalamic set point for body temperature regulation
Indication & Usage:
HBN-1 is intended for inducing regulated therapeutic hypothermia in adults resuscitated from cardiac arrest.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
HBN-1 was designed to induce therapeutic hypothermia, the intentional lowering of body temperature to help prevent brain injury. This would improve survival and neurological outcomes for patients who have had cardiac arrest. The injectable drug would help healthcare providers induce therapeutic hypothermia more efficiently.

Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Hypothalamic set point for body temperature regulation
HBN-1 is intended for inducing regulated therapeutic hypothermia in adults resuscitated from cardiac arrest.
2019 (FDA)
HBN-1 was designed to induce therapeutic hypothermia, the intentional lowering of body temperature to help prevent brain injury. This would improve survival and neurological outcomes for patients who have had cardiac arrest. The injectable drug would help healthcare providers induce therapeutic hypothermia more efficiently.
40

AXER-204
Protein
AXER-204 is intended to promote the recovery of neurological function through axonal fiber growth in adults with chronic spinal cord injury.
AXER-204
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
ReNetX Bio (formerly Axerion Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
ReNetX Bio (formerly Axerion Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
Target:
Nogo receptor pathway
Indication & Usage:
AXER-204 is intended to promote the recovery of neurological function through axonal fiber growth in adults with chronic spinal cord injury.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
AXER-204 promotes axonal growth and functional recovery in patients with chronic spinal cord injury, improving their neurological function and quality of life.

Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
Nogo receptor pathway
AXER-204 is intended to promote the recovery of neurological function through axonal fiber growth in adults with chronic spinal cord injury.
2019 (FDA)
AXER-204 promotes axonal growth and functional recovery in patients with chronic spinal cord injury, improving their neurological function and quality of life.
39

Fx-5A (KM-011)
Peptide
Fx-5A is intended for the treatment of congenital heart disease in adult patients with acute coronary syndrome, particularly those at high risk of myocardial infarction.
Fx-5A (KM-011)
 Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
Therapeutic Area:
Cardiopulmonary
Disease:
Atherosclerosis / Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
Target:
Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT) pathway
Indication & Usage:
Fx-5A is intended for the treatment of congenital heart disease in adult patients with acute coronary syndrome, particularly those at high risk of myocardial infarction.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
The Fx-5A peptide complex is a high-density lipoprotein mimic being studied for the treatment of cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death and disability in the United States. Fx-5A slows down atherosclerosis and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques, helping to prevent heart attacks in high-risk patients.

Atherosclerosis / Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT) pathway
Fx-5A is intended for the treatment of congenital heart disease in adult patients with acute coronary syndrome, particularly those at high risk of myocardial infarction.
2019 (FDA)
The Fx-5A peptide complex is a high-density lipoprotein mimic being studied for the treatment of cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death and disability in the United States. Fx-5A slows down atherosclerosis and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques, helping to prevent heart attacks in high-risk patients.
38

Nomlabofusp (CTI-1601)
Protein
Nomlabofusp is intended to slow the deterioration of the ability to walk in children and adults with Friedreich's ataxia.
Nomlabofusp (CTI-1601)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Chondrial Therapeutics (merged with Larimar Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Chondrial Therapeutics (merged with Larimar Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Friedreich's Ataxia (FRDA)
Target:
Mitochondria
Indication & Usage:
Nomlabofusp is intended to slow the deterioration of the ability to walk in children and adults with Friedreich's ataxia.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Nomlabofusp is a new protein replacement therapy that was made to address the underlying cause of Friedrich’s ataxia (FRDA), a rare inherited disease that causes progressive damage to the nervous system. Unlike other treatments for FRDA, nomlabofusp increases frataxin levels in the mitochondria, improving cellular function and slowing disease progression.

Friedreich's Ataxia (FRDA)
Mitochondria
Nomlabofusp is intended to slow the deterioration of the ability to walk in children and adults with Friedreich's ataxia.
2019 (FDA)
Nomlabofusp is a new protein replacement therapy that was made to address the underlying cause of Friedrich’s ataxia (FRDA), a rare inherited disease that causes progressive damage to the nervous system. Unlike other treatments for FRDA, nomlabofusp increases frataxin levels in the mitochondria, improving cellular function and slowing disease progression.
37
Benserazide (PB-04)
Small Molecule
Benserazide is intended to treat beta thalassemia in patients of all ages.
Benserazide (PB-04)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Phoenicia Biosciences
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Phoenicia Biosciences
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Beta Thalassemia
Target:
Transcriptional activator of fetal gamma-globin expression
Indication & Usage:
Benserazide is intended to treat beta thalassemia in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (Health Canada; FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Benserazide is an approved oral drug that is being repurposed to treat beta thalassemia, a blood disorder that decreases the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen. Benserazide can increase fetal globin levels in animal models, and this activity may be able to compensate for insufficient levels of hemoglobin A.

Beta Thalassemia
Transcriptional activator of fetal gamma-globin expression
Benserazide is intended to treat beta thalassemia in patients of all ages.
2019 (Health Canada; FDA)
Benserazide is an approved oral drug that is being repurposed to treat beta thalassemia, a blood disorder that decreases the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen. Benserazide can increase fetal globin levels in animal models, and this activity may be able to compensate for insufficient levels of hemoglobin A.
36
KER-047
Small Molecule
KER-047 is intended as an oral treatment for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) and iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA) in patients of all ages.
KER-047
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Keros Therapeutics; University of Houston; Brigham and Women's Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Keros Therapeutics; University of Houston; Brigham and Women's Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP)
Target:
Activin receptor-like kinase-2 (ALK2)
Indication & Usage:
KER-047 is intended as an oral treatment for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) and iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA) in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2019 (TGA (Australia); MEB (Netherlands))
Public Health Impact:
KER-047 is a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of activin receptor-like kinase 2 (ALK2) that is being developed for the treatment of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a rare condition in which muscle and connective tissues are replaced over time by bone, as well as iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia, a rare genetic disorder that causes iron deficiency in children. By blocking hyperactive ALK2 signaling, KER-047 may prevent inappropriate bone formation and reduce hepcidin, a hormone that regulates iron levels.

Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP)
Activin receptor-like kinase-2 (ALK2)
KER-047 is intended as an oral treatment for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) and iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA) in patients of all ages.
2019 (TGA (Australia); MEB (Netherlands))
KER-047 is a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of activin receptor-like kinase 2 (ALK2) that is being developed for the treatment of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a rare condition in which muscle and connective tissues are replaced over time by bone, as well as iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia, a rare genetic disorder that causes iron deficiency in children. By blocking hyperactive ALK2 signaling, KER-047 may prevent inappropriate bone formation and reduce hepcidin, a hormone that regulates iron levels.
35
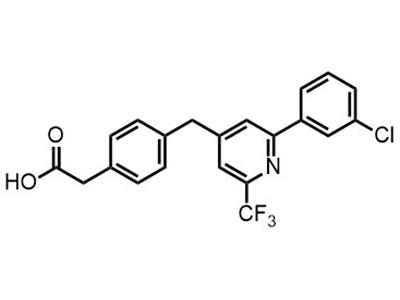
Zatolmilast (BPN14770)
Small Molecule
Zatolmilast is intended for the treatment of fragile X syndrome in adolescents and children.
Zatolmilast (BPN14770)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Tetra Discovery Partners (acquired by Shionogi)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Tetra Discovery Partners (acquired by Shionogi)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Fragile X Syndrome (FXS)
Target:
Phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D)
Indication & Usage:
Zatolmilast is intended for the treatment of fragile X syndrome in adolescents and children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2018 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Zatolmilast (BPN14770) is being studied to treat fragile X syndrome (FXS), a leading cause of inherited intellectual disability. Zatolmilast improves behavioral activity, social interaction, and brain cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels, addressing a key unmet medical need for new FXS therapies.

Fragile X Syndrome (FXS)
Phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D)
Zatolmilast is intended for the treatment of fragile X syndrome in adolescents and children.
2018 (FDA)
Zatolmilast (BPN14770) is being studied to treat fragile X syndrome (FXS), a leading cause of inherited intellectual disability. Zatolmilast improves behavioral activity, social interaction, and brain cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels, addressing a key unmet medical need for new FXS therapies.
34
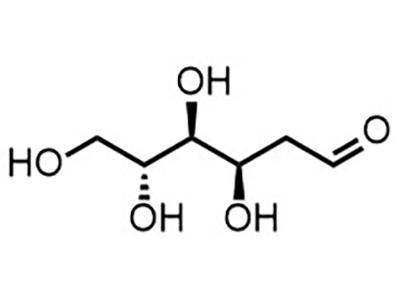
2DG (2-deoxy-glucose)
Small Molecule
2DG is intended for the treatment of epilepsy in pediatric and adult patients, including those with recurring seizures and medically intractable epilepsy.
2DG (2-deoxy-glucose)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Wisconsin, Madison (licensed to NeuroGenomeX, Inc.)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Wisconsin, Madison (licensed to NeuroGenomeX, Inc.)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Epilepsy
Target:
Glycolytic pathways in the brain
Indication & Usage:
2DG is intended for the treatment of epilepsy in pediatric and adult patients, including those with recurring seizures and medically intractable epilepsy.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2018 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
2-deoxy-glucose (2DG) is a glucose analog that has antiseizure effects in preclinical models and is being explored as a possible treatment for epilepsy. 2DG may reduce seizure frequency, impair the progression of kindled seizures, and possibly change the chronic effects of seizures, such as cognitive and memory dysfunction.

Epilepsy
Glycolytic pathways in the brain
2DG is intended for the treatment of epilepsy in pediatric and adult patients, including those with recurring seizures and medically intractable epilepsy.
2018 (FDA)
2-deoxy-glucose (2DG) is a glucose analog that has antiseizure effects in preclinical models and is being explored as a possible treatment for epilepsy. 2DG may reduce seizure frequency, impair the progression of kindled seizures, and possibly change the chronic effects of seizures, such as cognitive and memory dysfunction.
33
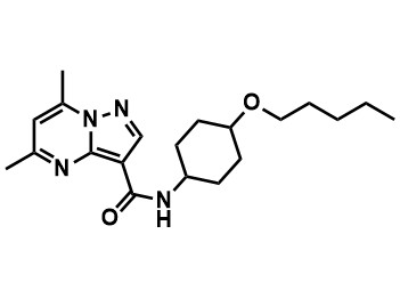
BIA 28-6156
Small Molecule
BIA 28-6156 is intended for use as a treatment for GBA-associated parkinsonism in adults.
BIA 28-6156
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Bial Biotech
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Bial Biotech
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Target:
Glucocerebrosidase (GCase)
Indication & Usage:
BIA 28-6156 is intended for use as a treatment for GBA-associated parkinsonism in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2020 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
BIA 28-6156 is a first-in-class compound designed to address the unmet need for treatments that target the primary causes of GBA-associated parkinsonism. Compromised glucocerebrosidase (GCase) enzyme activity is associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease, as well as accelerated disease progression. BIA 28-6156 is the first GCase enzyme activator to be studied in clinical trials.

Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Glucocerebrosidase (GCase)
BIA 28-6156 is intended for use as a treatment for GBA-associated parkinsonism in adults.
2020 (FDA)
BIA 28-6156 is a first-in-class compound designed to address the unmet need for treatments that target the primary causes of GBA-associated parkinsonism. Compromised glucocerebrosidase (GCase) enzyme activity is associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease, as well as accelerated disease progression. BIA 28-6156 is the first GCase enzyme activator to be studied in clinical trials.
32

AGIL-AADC
Gene Therapy
AGIL-AADC (now approved as KEBILIDI/Upstaza) is a gene therapy to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
AGIL-AADC
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Agilis Biotherapeutics (prior to acquisition by PTC Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Agilis Biotherapeutics (prior to acquisition by PTC Therapeutics)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Target:
Delivers the functional DDC gene directly to the putamen
Indication & Usage:
AGIL-AADC (now approved as KEBILIDI/Upstaza) is a gene therapy to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2017 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
AGIL-AADC (now approved as KEBILIDI/Upstaza) is a one-time gene replacement therapy made to treat L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency, a rare inherited disease that affects the central nervous system causing developmental delays, weak muscle tone, and inability to control movement of the limbs. AGIL-AADC increases dopamine and serotonin production, improving motor and cognitive functions and reducing severe symptoms.

Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Delivers the functional DDC gene directly to the putamen
AGIL-AADC (now approved as KEBILIDI/Upstaza) is a gene therapy to treat adults and children aged 18 months and older with severe aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
2017 (FDA)
AGIL-AADC (now approved as KEBILIDI/Upstaza) is a one-time gene replacement therapy made to treat L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency, a rare inherited disease that affects the central nervous system causing developmental delays, weak muscle tone, and inability to control movement of the limbs. AGIL-AADC increases dopamine and serotonin production, improving motor and cognitive functions and reducing severe symptoms.
31
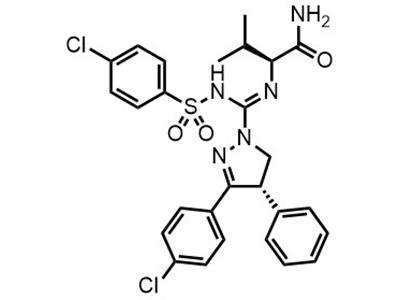
JD-5037
Small Molecule
JD-5037 is intended for the treatment of metabolic complications of obesity, specifically non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without insulin resistance, primarily in overweight adults.
JD-5037
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
Therapeutic Area:
Metabolic Disease
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
Therapeutic Area:
Metabolic Disease
Disease:
Metabolic Syndrome / Obesity
Target:
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R)
Indication & Usage:
JD-5037 is intended for the treatment of metabolic complications of obesity, specifically non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without insulin resistance, primarily in overweight adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2017 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
JD-5037 is a modulator of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 that improves metabolic abnormalities linked to obesity, such as reducing hepatic fat content, improving insulin sensitivity, and normalizing plasma lipid profiles without causing neuropsychiatric side effects.

Metabolic Syndrome / Obesity
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R)
JD-5037 is intended for the treatment of metabolic complications of obesity, specifically non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without insulin resistance, primarily in overweight adults.
2017 (FDA)
JD-5037 is a modulator of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 that improves metabolic abnormalities linked to obesity, such as reducing hepatic fat content, improving insulin sensitivity, and normalizing plasma lipid profiles without causing neuropsychiatric side effects.
30
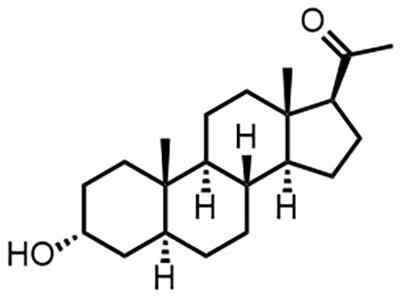
ALLO (Allopregnanolone)
Small Molecule
ALLO is intended to delay neurological impairments in pediatric patients with Niemann-Pick type C.
ALLO (Allopregnanolone)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Niemann-Pick C (NP-C)
Target:
GABA-ergic neurosteroid pathway
Indication & Usage:
ALLO is intended to delay neurological impairments in pediatric patients with Niemann-Pick type C.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2017 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
ALLO is a neurosteroid agent that is being studied for its potential to treat Niemann-Pick type C, a rare and progressive genetic disorder characterized by impaired lipid transport. ALLO may enhance neuron survival and reduce lipid accumulation in the brain, delaying neurological damage and increasing life span.

Niemann-Pick C (NP-C)
GABA-ergic neurosteroid pathway
ALLO is intended to delay neurological impairments in pediatric patients with Niemann-Pick type C.
2017 (FDA)
ALLO is a neurosteroid agent that is being studied for its potential to treat Niemann-Pick type C, a rare and progressive genetic disorder characterized by impaired lipid transport. ALLO may enhance neuron survival and reduce lipid accumulation in the brain, delaying neurological damage and increasing life span.
29

Actus-101
Gene Therapy
Actus-101 is intended for patients of all ages suffering from Pompe disease.
Actus-101
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Duke University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Duke University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Pompe Disease
Target:
Replacement of the acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) enzyme
Indication & Usage:
Actus-101 is intended for patients of all ages suffering from Pompe disease.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2016 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Actus-101 (AAV2/8-LSPhGAA) was designed as a one-time gene therapy treatment for Pompe disease, a rare genetic disorder of glycogen storage that causes progressive muscle weakness. Actus-101 aims to treat the implicated enzyme deficiency by continuous production of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) This is a more effective treatment than traditional enzyme replacement therapy.

Pompe Disease
Replacement of the acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) enzyme
Actus-101 is intended for patients of all ages suffering from Pompe disease.
2016 (FDA)
Actus-101 (AAV2/8-LSPhGAA) was designed as a one-time gene therapy treatment for Pompe disease, a rare genetic disorder of glycogen storage that causes progressive muscle weakness. Actus-101 aims to treat the implicated enzyme deficiency by continuous production of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) This is a more effective treatment than traditional enzyme replacement therapy.
28
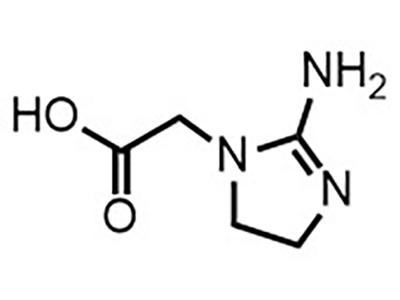
LUM-001
Small Molecule
LUM-001 is an oral therapeutic intended for treating creatine transporter deficiency (CTD) in patients of all ages.
LUM-001
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Lumos Pharma
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Lumos Pharma
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Creatine Transporter Deficiency
Target:
Cerebral creatine kinase pathway
Indication & Usage:
LUM-001 is an oral therapeutic intended for treating creatine transporter deficiency (CTD) in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2016 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
LUM-001(cyclocreatine) is a cyclic analog of creatine that can cross the blood–brain barrier. Cyclocreatine is an alternative energy source for patients with creatine transporter deficiency, a rare inherited disorder caused by a mutation in the creatine transporter protein.

Creatine Transporter Deficiency
Cerebral creatine kinase pathway
LUM-001 is an oral therapeutic intended for treating creatine transporter deficiency (CTD) in patients of all ages.
2016 (FDA)
LUM-001(cyclocreatine) is a cyclic analog of creatine that can cross the blood–brain barrier. Cyclocreatine is an alternative energy source for patients with creatine transporter deficiency, a rare inherited disorder caused by a mutation in the creatine transporter protein.
27

GM-CSF (inhaled formulation)
Protein
GM-CSF (now approved as Sargmalin®) is intended for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
GM-CSF (inhaled formulation)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Cincinnati Children's Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Cincinnati Children's Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Pulmonary
Disease:
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP)
Target:
Alveolar macrophages
Indication & Usage:
GM-CSF (now approved as Sargmalin®) is intended for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2016 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Nebulized granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (now approved as Sargmalin®) is intended to treat autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis by stimulating the patient’s immune cells. This lessens the need for invasive whole-lung lavage procedures that require general anesthesia and hospitalization. The inhaled formulation lets patients self-administer the therapy at home.

Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP)
Alveolar macrophages
GM-CSF (now approved as Sargmalin®) is intended for the treatment of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults and children.
2016 (FDA)
Nebulized granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (now approved as Sargmalin®) is intended to treat autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis by stimulating the patient’s immune cells. This lessens the need for invasive whole-lung lavage procedures that require general anesthesia and hospitalization. The inhaled formulation lets patients self-administer the therapy at home.
26

Vamorolone
Small Molecule
Vamorolone (now approved as Agamree) is a corticosteroid for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
Vamorolone
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
ReveraGen
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
ReveraGen
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Target:
Glucocorticoid receptor via unknown mechanism of action
Indication & Usage:
Vamorolone (now approved as Agamree) is a corticosteroid for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Vamorolone (now marketed as Agamree®) is a dissociative anti-inflammatory steroid (corticosteroid) that decouples positive therapeutic effects from some of the negative side effects linked to traditional corticosteroid use. It is for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a rare genetic childhood disease that gradually causes weakness and loss of muscle function.

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Glucocorticoid receptor via unknown mechanism of action
Vamorolone (now approved as Agamree) is a corticosteroid for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients aged 2 years and older.
2015 (FDA)
Vamorolone (now marketed as Agamree®) is a dissociative anti-inflammatory steroid (corticosteroid) that decouples positive therapeutic effects from some of the negative side effects linked to traditional corticosteroid use. It is for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a rare genetic childhood disease that gradually causes weakness and loss of muscle function.
25
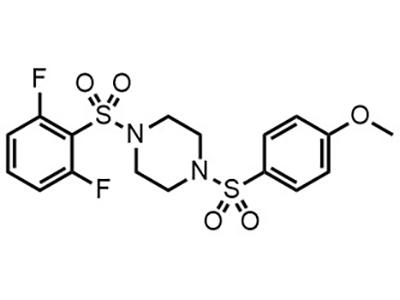
DASA-23
Small Molecule
DASA-23 is intended for use as a PET tracer to evaluate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) expression levels in adults.
DASA-23
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Stanford University
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Stanford University
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Glioblastoma
Target:
Pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 (PKM2)
Indication & Usage:
DASA-23 is intended for use as a PET tracer to evaluate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) expression levels in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
[18F]DASA-23 is a small molecule PET-imaging agent being studied for its potential to serve as a diagnostic tool for cancer. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) catalyzes the final irreversible step in glycolysis, which is a key step in tumor metabolism and growth. [18F]DASA-23 has demonstrated the visualization of aberrantly expressed PKM2 in human subjects.

Glioblastoma
Pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 (PKM2)
DASA-23 is intended for use as a PET tracer to evaluate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) expression levels in adults.
2015 (FDA)
[18F]DASA-23 is a small molecule PET-imaging agent being studied for its potential to serve as a diagnostic tool for cancer. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) catalyzes the final irreversible step in glycolysis, which is a key step in tumor metabolism and growth. [18F]DASA-23 has demonstrated the visualization of aberrantly expressed PKM2 in human subjects.
24

PF614
Small Molecule
PF614 is an oral therapy designed for the treatment of moderate to severe pain in adults.
PF614
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Ensyce Bioscience
Therapeutic Area:
Pain
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Ensyce Bioscience
Therapeutic Area:
Pain
Disease:
Severe pain
Target:
Mu-opioid receptor pathway
Indication & Usage:
PF614 is an oral therapy designed for the treatment of moderate to severe pain in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
PF614 is a next-generation opioid designed to limit overdose potential. A prodrug of oxycodone, PF614 brings effective pain relief while preventing both oral and non-oral abuse, reducing the risk of opioid addiction and related societal burdens.

Severe pain
Mu-opioid receptor pathway
PF614 is an oral therapy designed for the treatment of moderate to severe pain in adults.
2015 (FDA)
PF614 is a next-generation opioid designed to limit overdose potential. A prodrug of oxycodone, PF614 brings effective pain relief while preventing both oral and non-oral abuse, reducing the risk of opioid addiction and related societal burdens.
23

AAVIL-1Ra
Gene Therapy
AAVIL-1Ra is intended for treating osteoarthritis in adults with mid-stage disease, focusing on those who experience significant pain and joint degradation.
AAVIL-1Ra
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Therapeutic Area:
Rheumatology
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Therapeutic Area:
Rheumatology
Disease:
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Target:
Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)
Indication & Usage:
AAVIL-1Ra is intended for treating osteoarthritis in adults with mid-stage disease, focusing on those who experience significant pain and joint degradation.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
The AAVIL-1Ra gene therapy was designed as a treatment for osteoarthritis. By delivering the IL-1Ra gene directly to the joints, expression of IL-1Ra protein reduces inflammation, pain, and cartilage loss and may improve joint function and quality of life for patients.

Osteoarthritis (OA)
Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)
AAVIL-1Ra is intended for treating osteoarthritis in adults with mid-stage disease, focusing on those who experience significant pain and joint degradation.
2015 (FDA)
The AAVIL-1Ra gene therapy was designed as a treatment for osteoarthritis. By delivering the IL-1Ra gene directly to the joints, expression of IL-1Ra protein reduces inflammation, pain, and cartilage loss and may improve joint function and quality of life for patients.
22

Avexitide (Exendin-(9-39))
Peptide
Avexitide is intended for the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism in children and adults who suffer from severe hypoglycemia unresponsive to existing medical therapies.
Avexitide (Exendin-(9-39))
 Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Modality:
Peptide
Partner(s):
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Congenital Hyperinsulinism (HI)
Target:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1r)
Indication & Usage:
Avexitide is intended for the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism in children and adults who suffer from severe hypoglycemia unresponsive to existing medical therapies.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Avexitide is being studied for the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism, the most common cause of persistent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in children and infants. Avexitide acts by preventing excessive insulin secretion, raising fasting blood glucose levels and preventing hypoglycemia.

Congenital Hyperinsulinism (HI)
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1r)
Avexitide is intended for the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism in children and adults who suffer from severe hypoglycemia unresponsive to existing medical therapies.
2015 (FDA)
Avexitide is being studied for the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism, the most common cause of persistent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in children and infants. Avexitide acts by preventing excessive insulin secretion, raising fasting blood glucose levels and preventing hypoglycemia.
21

Retinal Progenitor Cells
Cell Therapy
Retinal progenitor cells are intended for retinitis pigmentosa patients and patients progressing to legal blindness.
Retinal Progenitor Cells
 Modality:
Cell Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, Irvine
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Modality:
Cell Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, Irvine
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
Target:
Grafted retinal progenitor cells (RPCs)
Indication & Usage:
Retinal progenitor cells are intended for retinitis pigmentosa patients and patients progressing to legal blindness.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) are being studied to treat retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a common inherited disease affecting the retina causing progressive and eventually severe visual impairment. RPCs may improve vision and prevent blindness in RP patients by promoting the function of affected photoreceptors and generating new photoreceptors.

Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
Grafted retinal progenitor cells (RPCs)
Retinal progenitor cells are intended for retinitis pigmentosa patients and patients progressing to legal blindness.
2015 (FDA)
Retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) are being studied to treat retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a common inherited disease affecting the retina causing progressive and eventually severe visual impairment. RPCs may improve vision and prevent blindness in RP patients by promoting the function of affected photoreceptors and generating new photoreceptors.
20

Quilseconazole (VT-1129)
Small Molecule
Quilseconazole is an antifungal agent intended for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis.
Quilseconazole (VT-1129)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Cryptococcal Meningitis
Target:
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Indication & Usage:
Quilseconazole is an antifungal agent intended for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2015 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Quilseconazole is an orally active antifungal agent that binds with high affinity and specificity to the cryptococcal cytochrome P450 enzyme 51. It is being explored as a treatment for cryptococcal meningitis (CM), a sometimes fatal infection of the tissues around the brain and spinal cord. CM is the second leading cause of HIV-related deaths in sub-Saharan Africa, and current therapies are only marginally effective.

Cryptococcal Meningitis
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Quilseconazole is an antifungal agent intended for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis.
2015 (FDA)
Quilseconazole is an orally active antifungal agent that binds with high affinity and specificity to the cryptococcal cytochrome P450 enzyme 51. It is being explored as a treatment for cryptococcal meningitis (CM), a sometimes fatal infection of the tissues around the brain and spinal cord. CM is the second leading cause of HIV-related deaths in sub-Saharan Africa, and current therapies are only marginally effective.
19
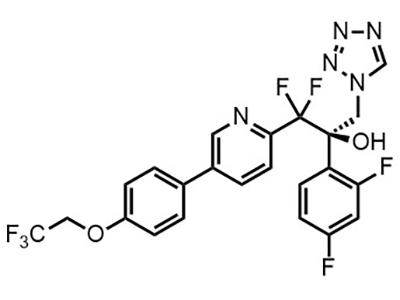
Oteseconazole (VT-1161)
Small Molecule
Oteseconazole (VT-1161) is an antifungal medication (now approved as Vivjoa®) for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
Oteseconazole (VT-1161)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
Reproductive Health
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mycovia Pharmaceuticals (formerly Viamet)
Therapeutic Area:
Reproductive Health
Disease:
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis
Target:
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Indication & Usage:
Oteseconazole (VT-1161) is an antifungal medication (now approved as Vivjoa®) for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2016 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Oteseconazole (now approved as Vivjoa®) is an oral antifungal medicine that treats chronic yeast infection by inhibiting the growth and spread of fungi. It blocks the cytochrome P450 enzyme 51 in microbes while having lower affinity for the human variant, helping minimize off-target toxicity.

Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis
Fungal lanosterol demethylase (LD, aka CYP51)
Oteseconazole (VT-1161) is an antifungal medication (now approved as Vivjoa®) for the treatment of recurrent vaginal yeast infections in females who are not and cannot become pregnant.
2016 (FDA)
Oteseconazole (now approved as Vivjoa®) is an oral antifungal medicine that treats chronic yeast infection by inhibiting the growth and spread of fungi. It blocks the cytochrome P450 enzyme 51 in microbes while having lower affinity for the human variant, helping minimize off-target toxicity.
18

AAV2-AADC
Gene Therapy
AAV2-AADC gene therapy is intended for the treatment of AADC deficiency in children.
AAV2-AADC
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Target:
Biosynthesis of catecholamines
Indication & Usage:
AAV2-AADC gene therapy is intended for the treatment of AADC deficiency in children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2014 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
AAV2-AADC gene therapy is being studied to treat aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency, a rare genetic disorder. Delivery of the functional gene restores AADC enzyme activity, improving dopamine and serotonin production, thereby reducing the neurological symptoms of AADC deficiency in children.

Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase (AADC) Deficiency
Biosynthesis of catecholamines
AAV2-AADC gene therapy is intended for the treatment of AADC deficiency in children.
2014 (FDA)
AAV2-AADC gene therapy is being studied to treat aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency, a rare genetic disorder. Delivery of the functional gene restores AADC enzyme activity, improving dopamine and serotonin production, thereby reducing the neurological symptoms of AADC deficiency in children.
17

P-321
Small Molecule
P-321 is intended for the treatment of dry eye disease in adults and potentially children.
P-321
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Parion Sciences
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Parion Sciences
Therapeutic Area:
Ophthalmology
Disease:
Dry Eye Disease (DED)
Target:
Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)
Indication & Usage:
P-321 is intended for the treatment of dry eye disease in adults and potentially children.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2014 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
P-321 is a potent small molecule inhibitor of epithelial sodium channels on the eye’s surface. The compound is meant to treat dry eye disease by increasing tear production and keeping the eye surface moister, reducing symptoms of eye discomfort and damage.

Dry Eye Disease (DED)
Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)
P-321 is intended for the treatment of dry eye disease in adults and potentially children.
2014 (FDA)
P-321 is a potent small molecule inhibitor of epithelial sodium channels on the eye’s surface. The compound is meant to treat dry eye disease by increasing tear production and keeping the eye surface moister, reducing symptoms of eye discomfort and damage.
16
Biomimetic Actinide Decorporation Agents
Small Molecule
The decorporation agents 3,4,3-LI-1,2-HOPO and 5-LIO-Me-3,2-HOPO are intended for treating radioisotope contamination in all age groups, particularly following events like dirty bomb attacks.
Biomimetic Actinide Decorporation Agents
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of California, Berkeley
Therapeutic Area:
Radioisotope Contamination
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of California, Berkeley
Therapeutic Area:
Radioisotope Contamination
Disease:
Biodefense / Radiation Countermeasure
Target:
Actinides and lanthanides
Indication & Usage:
The decorporation agents 3,4,3-LI-1,2-HOPO and 5-LIO-Me-3,2-HOPO are intended for treating radioisotope contamination in all age groups, particularly following events like dirty bomb attacks.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2014 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
The decorporation agents 3,4,3-LI-1,2-HOPO and 5-LIO-Me-3,2-HOPO are up to 30 times more effective than the current standard of care for radiation exposure (diethylenetriamine pentaacetate, DTPA) and are orally active, greatly improving the treatment of radioisotope contamination.

Biodefense / Radiation Countermeasure
Actinides and lanthanides
The decorporation agents 3,4,3-LI-1,2-HOPO and 5-LIO-Me-3,2-HOPO are intended for treating radioisotope contamination in all age groups, particularly following events like dirty bomb attacks.
2014 (FDA)
The decorporation agents 3,4,3-LI-1,2-HOPO and 5-LIO-Me-3,2-HOPO are up to 30 times more effective than the current standard of care for radiation exposure (diethylenetriamine pentaacetate, DTPA) and are orally active, greatly improving the treatment of radioisotope contamination.
15

AAV2-GDNF
Gene Therapy
AAV2-GDNF is intended to protect and restore dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra as a treatment for adults with Parkinson's disease.
AAV2-GDNF
 Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Gene Therapy
Partner(s):
University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Target:
Delivery of glial cell-line derived neurotropic factor (GDNF) to dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra
Indication & Usage:
AAV2-GDNF is intended to protect and restore dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra as a treatment for adults with Parkinson's disease.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2012 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
AAV2-GDNF gene therapy aims to protect and restore dopaminergic neurons by increasing levels of glial cell-line derived neurotropic factor (GDNF), a naturally occurring growth factor that promotes nerve cell survival. By this mechanism, AAV2-GDNF may reverse the movement and psychological symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease.

Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Delivery of glial cell-line derived neurotropic factor (GDNF) to dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra
AAV2-GDNF is intended to protect and restore dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra as a treatment for adults with Parkinson's disease.
2012 (FDA)
AAV2-GDNF gene therapy aims to protect and restore dopaminergic neurons by increasing levels of glial cell-line derived neurotropic factor (GDNF), a naturally occurring growth factor that promotes nerve cell survival. By this mechanism, AAV2-GDNF may reverse the movement and psychological symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease.
14

Adrabetadex (VTS-270)
Macromolecule
VTS-270 is intended to lower cholesterol and decrease lipid accumulation in early childhood patients with Niemann-Pick Type C.
Adrabetadex (VTS-270)
 Modality:
Macromolecule
Partner(s):
Vtesse Pharma LLC
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Macromolecule
Partner(s):
Vtesse Pharma LLC
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Niemann-Pick C (NP-C)
Target:
Cholesterol and lipid accumulation pathway in lysosomes
Indication & Usage:
Adrabetadex (VTS-270) is intended to lower cholesterol and decrease lipid accumulation in early childhood patients with Niemann-Pick Type C.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2012 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Adrabetadex could be a treatment for Niemann-Pick type C, a rare inherited lysosomal storage disease that affects the body’s ability to process cholesterol and other lipids and for which there is no cure. Adrabetadex reduces cholesterol and lipid accumulation and may prolong survival by slowing the progression of neurological symptoms.

Niemann-Pick C (NP-C)
Cholesterol and lipid accumulation pathway in lysosomes
Adrabetadex (VTS-270) is intended to lower cholesterol and decrease lipid accumulation in early childhood patients with Niemann-Pick Type C.
2012 (FDA)
Adrabetadex could be a treatment for Niemann-Pick type C, a rare inherited lysosomal storage disease that affects the body’s ability to process cholesterol and other lipids and for which there is no cure. Adrabetadex reduces cholesterol and lipid accumulation and may prolong survival by slowing the progression of neurological symptoms.
13
DEX-M74 (ManNAc)
Small Molecule
DEX-M74 is intended for the treatment of GNE myopathy in patients aged 18-70 years.
DEX-M74 (ManNAc)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
NHGRI; New Zealand Pharmaceuticals
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
NHGRI; New Zealand Pharmaceuticals
Therapeutic Area:
Musculoskeletal
Disease:
GNE Myopathy
Target:
Supplementation of N-acetyl-D-mannosamine
Indication & Usage:
DEX-M74 is intended for the treatment of GNE myopathy in patients aged 18-70 years.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2012 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
DEX-M74 is being studied as a potential treatment for GNE myopathy, a rare degenerative muscle disease for which there is no existing therapy. DEX-M74 may restore sialylation of muscle proteins, possibly leading to increased muscle function.

GNE Myopathy
Supplementation of N-acetyl-D-mannosamine
DEX-M74 is intended for the treatment of GNE myopathy in patients aged 18-70 years.
2012 (FDA)
DEX-M74 is being studied as a potential treatment for GNE myopathy, a rare degenerative muscle disease for which there is no existing therapy. DEX-M74 may restore sialylation of muscle proteins, possibly leading to increased muscle function.
12
EPI01
Small Molecule
EPI01 is intended for the treatment of sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia in patients of all ages, particularly those who require chronic treatment.
EPI01
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Cleveland Clinic (prior to new company, EpiDestiny, which was acquired by NovoNordisk)
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Cleveland Clinic (prior to new company, EpiDestiny, which was acquired by NovoNordisk)
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
Target:
DNA methyltransferase enzyme 1 (DNMT1) and cytidine deaminase
Indication & Usage:
EPI01 is intended for the treatment of sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia in patients of all ages, particularly those who require chronic treatment.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2011 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
EPI01 is an oral, fixed-dose formulation of decitabine and tetrahydrouridine that may increase fetal hemoglobin levels, replacing defective hemoglobin and reducing the complications of sickle cell disease (SCD) and improving clinical outcomes for patients with SCD and beta thalassemia.

Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
DNA methyltransferase enzyme 1 (DNMT1) and cytidine deaminase
EPI01 is intended for the treatment of sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia in patients of all ages, particularly those who require chronic treatment.
2011 (FDA)
EPI01 is an oral, fixed-dose formulation of decitabine and tetrahydrouridine that may increase fetal hemoglobin levels, replacing defective hemoglobin and reducing the complications of sickle cell disease (SCD) and improving clinical outcomes for patients with SCD and beta thalassemia.
11

Filociclovir (MBX-400)
Small Molecule
Filociclovir is intended for the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompromised patients of all ages, including bone marrow and solid-organ transplant recipients.
Filociclovir (MBX-400)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Wayne State University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Wayne State University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Target:
Viral DNA polymerase
Indication & Usage:
Filociclovir is intended for the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompromised patients of all ages, including bone marrow and solid-organ transplant recipients.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2011 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Filociclovir is a potent inhibitor of cytomegalovirus (CMV) that works against drug-resistant strains and a broad range of beta- and gamma-herpesviruses. It is a promising new option to treat CMV with fewer toxic side effects.

Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Viral DNA polymerase
Filociclovir is intended for the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompromised patients of all ages, including bone marrow and solid-organ transplant recipients.
2011 (FDA)
Filociclovir is a potent inhibitor of cytomegalovirus (CMV) that works against drug-resistant strains and a broad range of beta- and gamma-herpesviruses. It is a promising new option to treat CMV with fewer toxic side effects.
10
Auranofin
Small Molecule
Auranofin is intended primarily for middle-aged adults with relapsed or treatment-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Auranofin
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Kansas Medical Center; The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Kansas Medical Center; The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
Therapeutic Area:
Oncology
Disease:
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Target:
Thioredoxin reductase pathway
Indication & Usage:
Auranofin is intended primarily for middle-aged adults with relapsed or treatment-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2011 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Auranofin, a U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved compound to treat rheumatoid arthritis, was reformulated and is being studied as a potential antitumor drug for relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Auranofin selectively induces apoptosis in CLL cells.

Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Thioredoxin reductase pathway
Auranofin is intended primarily for middle-aged adults with relapsed or treatment-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
2011 (FDA)
Auranofin, a U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved compound to treat rheumatoid arthritis, was reformulated and is being studied as a potential antitumor drug for relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Auranofin selectively induces apoptosis in CLL cells.
9
Aes-103 (5-HMF)
Small Molecule
Aes-103 is intended to treat sickle cell disease in patients of all ages.
Aes-103 (5-HMF)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
AesRx, LLC (acquired by Baxter Pharmaceuticals)
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
AesRx, LLC (acquired by Baxter Pharmaceuticals)
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
Target:
Sickle hemoglobin (HbS)
Indication & Usage:
Aes-103 is intended to treat sickle cell disease in patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2011 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Aes-103 (5-HMF) is a first-in-class oral small molecule compound specifically designed to target the underlying mechanism of sickle cell disease, a genetic blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Aes-103 reduces the sickling of red blood cells by binding directly to hemoglobin, inducing a change to its structure.

Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
Sickle hemoglobin (HbS)
Aes-103 is intended to treat sickle cell disease in patients of all ages.
2011 (FDA)
Aes-103 (5-HMF) is a first-in-class oral small molecule compound specifically designed to target the underlying mechanism of sickle cell disease, a genetic blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Aes-103 reduces the sickling of red blood cells by binding directly to hemoglobin, inducing a change to its structure.
8
SPINALON
Small Molecule
Spinalon is intended for use in adults with chronic motor-complete spinal cord injury to induce locomotor movements and mitigate paralysis-related health issues.
SPINALON
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Universite Laval
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Universite Laval
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
Target:
Central Pattern Generator (CPG) in the lumbar spinal cord
Indication & Usage:
Spinalon is intended for use in adults with chronic motor-complete spinal cord injury to induce locomotor movements and mitigate paralysis-related health issues.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2010 (Health Canada)
Public Health Impact:
SPINALON is an oral combined formulation of buspirone, carbidopa, and levodopa that activates the spinal locomotor network, improving stepping movements in motor-complete spinal cord injury patients. SPINALON may prevent or reverse health deterioration linked to chronic immobility.

Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
Central Pattern Generator (CPG) in the lumbar spinal cord
Spinalon is intended for use in adults with chronic motor-complete spinal cord injury to induce locomotor movements and mitigate paralysis-related health issues.
2010 (Health Canada)
SPINALON is an oral combined formulation of buspirone, carbidopa, and levodopa that activates the spinal locomotor network, improving stepping movements in motor-complete spinal cord injury patients. SPINALON may prevent or reverse health deterioration linked to chronic immobility.
7
Refanalin (ANG-3777)
Small Molecule
Refanalin is intended for adults with hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis resulting from chronic liver diseases including hepatitis C, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and other causes of liver fibrosis.
Refanalin (ANG-3777)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
Therapeutic Area:
Hepatology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
Therapeutic Area:
Hepatology
Disease:
Hepatic Fibrosis
Target:
c-Met receptor
Indication & Usage:
Refanalin is intended for adults with hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis resulting from chronic liver diseases including hepatitis C, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and other causes of liver fibrosis.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2010 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Refanalin is a small molecule that mimics the activity of hepatocyte growth factor. In preclinical models, it reduces hepatic fibrosis by reducing profibrotic gene expression and increasing the rate of collagen catabolism, improving liver function and preventing progression to cirrhosis.

Hepatic Fibrosis
c-Met receptor
Refanalin is intended for adults with hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis resulting from chronic liver diseases including hepatitis C, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and other causes of liver fibrosis.
2010 (FDA)
Refanalin is a small molecule that mimics the activity of hepatocyte growth factor. In preclinical models, it reduces hepatic fibrosis by reducing profibrotic gene expression and increasing the rate of collagen catabolism, improving liver function and preventing progression to cirrhosis.
6
JDTic
Small Molecule
JDTic is intended for the treatment of drug abuse (cocaine relapse), depression, and schizophrenia in adults.
JDTic
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Research Triangle Institute
Therapeutic Area:
Addiction/Overdose
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Research Triangle Institute
Therapeutic Area:
Addiction/Overdose
Disease:
Drug Abuse
Target:
Opioid kappa receptor
Indication & Usage:
JDTic is intended for the treatment of drug abuse (cocaine relapse), depression, and schizophrenia in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2009 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
JDTic was designed as a potential therapy for addiction, a major unmet public health need. JDTic is an inhibitor of the kappa opioid receptor (KOR) that shows greater potency and selectivity than other KOR antagonists. JDTic is being studied for its potential to prevent relapse of cocaine use, reduce depression, and relieve symptoms of schizophrenia.

Drug Abuse
Opioid kappa receptor
JDTic is intended for the treatment of drug abuse (cocaine relapse), depression, and schizophrenia in adults.
2009 (FDA)
JDTic was designed as a potential therapy for addiction, a major unmet public health need. JDTic is an inhibitor of the kappa opioid receptor (KOR) that shows greater potency and selectivity than other KOR antagonists. JDTic is being studied for its potential to prevent relapse of cocaine use, reduce depression, and relieve symptoms of schizophrenia.
5
SRX246
Small Molecule
SRX246 is intended for the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults.
SRX246
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Lehigh University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Lehigh University
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Depression
Target:
Vasopressin 1a (V1a) receptor
Indication & Usage:
SRX246 is intended for the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2009 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
SRX246 is a first-in-class brain-penetrant small molecule shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by blocking vasopressin 1a receptors, normalizing hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function and relieving chronic stress effects. This compound may lead to a new way to treat depression.

Depression
Vasopressin 1a (V1a) receptor
SRX246 is intended for the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults.
2009 (FDA)
SRX246 is a first-in-class brain-penetrant small molecule shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by blocking vasopressin 1a receptors, normalizing hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function and relieving chronic stress effects. This compound may lead to a new way to treat depression.
4
CDD-0102 (MCD-386)
Small Molecule
CDD-0102 is intended for the treatment of memory and cognitive deficits in adults with Alzheimer’s disease.
CDD-0102 (MCD-386)
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Toledo
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Toledo
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
Target:
M1 muscarinic receptors
Indication & Usage:
CDD-0102 is intended for the treatment of memory and cognitive deficits in adults with Alzheimer’s disease.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2008 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
CDD-0102 is a small molecule agonist of the M1 muscarinic receptor. In preclinical models of Alzheimer’s disease, CDD-0102 improved memory function, reduced β-amyloid formation and protected neurons from apoptosis.

Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
M1 muscarinic receptors
CDD-0102 is intended for the treatment of memory and cognitive deficits in adults with Alzheimer’s disease.
2008 (FDA)
CDD-0102 is a small molecule agonist of the M1 muscarinic receptor. In preclinical models of Alzheimer’s disease, CDD-0102 improved memory function, reduced β-amyloid formation and protected neurons from apoptosis.
3
EPI-A0001
Small Molecule
EPI-A0001 is intended for adolescents and adults diagnosed with Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA).
EPI-A0001
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Pennsylvania
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
University of Pennsylvania
Therapeutic Area:
CNS/Neuroscience
Disease:
Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA)
Target:
Mitochondrial redox centers
Indication & Usage:
EPI-A0001 is intended for adolescents and adults diagnosed with Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA).
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2008 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
EPI-A0001 is a strong antioxidant that improves mitochondrial function in Friedrich’s ataxia, a rare, inherited, progressive neurodegenerative movement disorder. By strengthening redox coupling, reducing oxidative stress, increasing ATP production, and decreasing lactate formation, EPI-A0001 may improve neurologic function.

Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA)
Mitochondrial redox centers
EPI-A0001 is intended for adolescents and adults diagnosed with Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA).
2008 (FDA)
EPI-A0001 is a strong antioxidant that improves mitochondrial function in Friedrich’s ataxia, a rare, inherited, progressive neurodegenerative movement disorder. By strengthening redox coupling, reducing oxidative stress, increasing ATP production, and decreasing lactate formation, EPI-A0001 may improve neurologic function.
2

Metastin (kisspeptin)
Protein
Metastin is intended for use in male and female patients of all ages with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) and other disorders related to abnormal GnRH secretion.
Metastin (kisspeptin)
 Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Modality:
Protein
Partner(s):
Massachusetts General Hospital
Therapeutic Area:
Endocrine
Disease:
Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (IHH)
Target:
G-protein-coupled receptor 54 (GPR54)
Indication & Usage:
Metastin is intended for use in male and female patients of all ages with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) and other disorders related to abnormal GnRH secretion.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2008 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
Metastin is a peptide that is important for human reproduction. It stimulates the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, modulating puberty onset and possibly treating reproductive disorders, such as idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.

Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (IHH)
G-protein-coupled receptor 54 (GPR54)
Metastin is intended for use in male and female patients of all ages with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) and other disorders related to abnormal GnRH secretion.
2008 (FDA)
Metastin is a peptide that is important for human reproduction. It stimulates the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, modulating puberty onset and possibly treating reproductive disorders, such as idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
1
ST20
Small Molecule
ST20 is intended as an oral treatment for beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease (SCD) for patients of all ages.
ST20
 Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Boston University School of Medicine
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Modality:
Small Molecule
Partner(s):
Boston University School of Medicine
Therapeutic Area:
Hematology
Disease:
Beta Thalassemia
Target:
Fetal globin gene expression
Indication & Usage:
ST20 is intended as an oral treatment for beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease (SCD) for patients of all ages.
Approval or Clearance Date(s):
2007 (FDA)
Public Health Impact:
ST20 is a short-chain fatty acid that induces fetal hemoglobin production. It increases total hemoglobin levels and reduces anemia in patients with beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease (SCD). Beta thalassemia and SCD are two of the most common genetic blood disorders, and current standard of care often involves regular blood transfusions or a bone marrow transplant.

Beta Thalassemia
Fetal globin gene expression
ST20 is intended as an oral treatment for beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease (SCD) for patients of all ages.
2007 (FDA)
ST20 is a short-chain fatty acid that induces fetal hemoglobin production. It increases total hemoglobin levels and reduces anemia in patients with beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease (SCD). Beta thalassemia and SCD are two of the most common genetic blood disorders, and current standard of care often involves regular blood transfusions or a bone marrow transplant.


