Translational Science Spectrum
The spectrum represents the stages of research involved in bringing more treatments to all people more quickly.
About the Translational Science Spectrum
The translational science spectrum shows the stages of translational research. The stages do not happen in a straight line or in one direction. Each stage builds upon and informs the others. At all stages, our staff and grantees come up with new approaches, prove their usefulness and share the findings. Patient involvement is a key feature of all stages in translation.
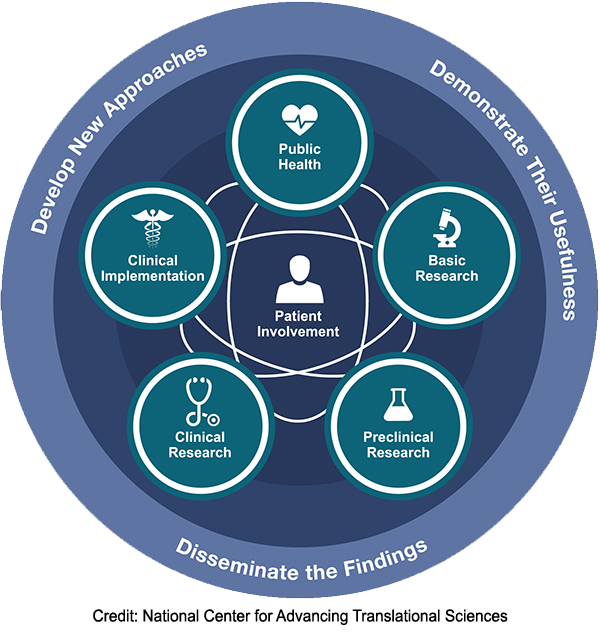
Basic Research
Basic research involves scientific exploration that can reveal fundamental mechanisms of biology, disease or behavior. Every stage of the translational research spectrum builds upon and informs basic research. NCATS scientists typically do not conduct basic research; however, insights gained from the center’s studies along the translational spectrum can inform basic research.
Preclinical Research
Preclinical research connects the basic science of disease with human medicine. During this stage, scientists develop model interventions to further understand the basis of a disease or disorder and find ways to treat it. Testing is carried out using cell or animal models of disease; samples of human or animal tissues; or computer-assisted simulations of drug, device or diagnostic interactions within living systems.
Clinical Research
Clinical research includes studies to better understand a disease in humans and relate this knowledge to findings in cell or animal models; testing and refinement of new technologies in people; testing of interventions for safety and effectiveness in those with or without disease; behavioral and observational studies; and outcomes and health services research. The goal of many clinical trials is to obtain data to support regulatory approval for an intervention.
Related Research
Clinical Implementation
Clinical implementation involves the adoption of interventions that have been demonstrated to be useful in a research environment into routine clinical care for the general population. This stage also includes implementation research to evaluate the results of clinical trials and to identify new clinical questions and gaps in care.
Related Research
Public Health
Public health includes studying health outcomes at the population level to determine the effects of diseases and efforts to prevent, diagnose and treat them. Findings help guide scientists working to assess the effects of current interventions and to develop new ones.
Related Research
About Translational Science

Translational Science Education Resources
We offer a collection of helpful educational resources and virtual classes to advance your knowledge of translational science.

Translational Science Principles
Our translational science principals characterize effective translational science approaches.

About Translational Science
Translational science focuses on understanding the scientific principles underlying each step of the translational process.


