Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory
The Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory studies ways to find molecules that can target genes, proteins, and pathways involved in various human diseases, including genetic, chronic, and infectious illnesses.
About the Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory
The Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory investigates concepts and strategies to identify molecular modalities targeting genes, proteins and pathway networks implicated a range of human disorders, including genetically inherited, chronic and infectious diseases.
To enable and optimize early-stage lead discovery, our Assay Development and Screening Technology (ADST) program specializes in the design of biochemical, cellular and microorganism-based assays that drive the high-throughput pharmacological testing of a variety of chemical classes, including approved drugs and novel composition of matter libraries. Assays have been designed to measure biological processes, including gene expression, posttranslational regulation, signaling and metabolism for disorders ranging from neuropathies and cancer to infectious diseases such as malaria and tuberculosis.
Research Projects
Our projects have involved multi-institutional collaborative efforts, including participation from intramural NIH and academic university laboratories, as well as disease foundations and biotechnology companies. Projects often incorporate new technologies to test in drug discovery settings. For example, we collaborated with the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) Association to implement a novel reporter gene system created to reduce the incidence of false positives/negatives from high-throughput screening (HTS). The team genome edited this ‘coincidence reporter’ into neuronal or Schwann cell types, respectively. These cell lines were used to model gene-dosage disorders related to Parkinson's disease or CMT type 1A peripheral neuropathy, enabling defined disease systems for quantitative high throughput screening (qHTS).
Laboratory Functions
The Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory sections are:
Assay Development and Screening Technology (ADST)
- Design, development and validation of phenotypic assays aimed at measuring cellular functions often modeling disease states. Examples have included novel reporter gene cell lines (e.g., Hasson, Fogel et al. 2015; Martinez, Braisted et al. 2021) and development of a non-mammalian model organism high-throughput screening platform to investigate fundamental molecular mechanisms of human disease (Dranchak, Oliphant et al. 2023).
- Design, development and validation of biochemical assays for molecular targets using a broad range of technologies. Currently we are focused on exploring the scope of our recently described structural dynamics response (SDR) assay platform (Ciulla, Dranchak et al. 2025) through collaborative projects with laboratories targeting proteins for therapeutic indications.
Chemical Biology
- Discovery and design of molecular modalities defining new chemical probe mechanisms and approaches to drug development. Current areas of investigation include mining the potent and selective inhibitors for several so-called ‘undruggable’ targets from vast nucleic acid-encoded macrocyclic peptide libraries (van Neer, Dranchak et al. 2025; van Neer, Dranchak et al. 2022). We are also exploring targeted protein degraders as applied to new antifolate-based therapeutics for oncology, immunology and microbe-based infectious diseases (Rana, Dranchak et al. 2024).
Training
- The laboratory offers multidisciplinary training opportunities for postdoctoral fellows, postbaccalaureate Intramural Research Training Award (IRTA) recipients and summer interns. Candidates interested in postdoctoral positions with proficiency in one or more of the following disciplines: biochemistry, molecular and cell biology and/or organic synthetic chemistry, and interested in research at the interface of chemical biology and drug discovery are encouraged to inquire for more information.
Our Team
Staff
Patricia Dranchak, Ph.D.
Mahesh Aitha, Ph.D.
Erin Oliphant, MFS
Current Trainees
Dan Ciulla, Ph.D. (postdoctoral fellow)
Abby Davis, (postbaccalaureate IRTA)
Publications
Browse a listing of Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory-related, peer-reviewed scientific publications that feature research supported by NCATS programs and initiatives.
- PubMed — National Library of Medicine (NLM) citations of biomedical and life sciences literature
- NCBI — National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Google Scholar — Research publications and citations
News
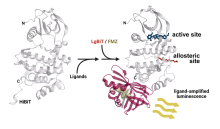
New Assay Technology Could Reshape Approach to Drug Discovery
June 3, 2025 - NCATS News
- Our Impact on Tools and Technologies
- Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory
NIH researchers created a test based on the natural vibrations of proteins that could help improve the search for drugs to treat a wide range of diseases.
Read Article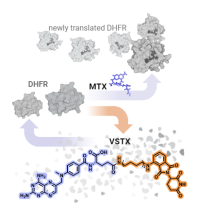
Retooled Methotrexate Could Lead to New Therapies for Cancer, Autoimmune Disorders
February 2, 2024 - NCATS News
- Chemistry Technology
- Preclinical Chemical Biology Laboratory
An NCATS-led team built a version of methotrexate that could lead to new tools to find new treatments for cancer, autoimmune disorders and rare diseases.
Read ArticleRelated Research
Analytical Chemistry
Discover NCATS' groundbreaking work in analytical chemistry, driving advancements in research. Explore innovative approaches and technologies aimed at enhancing drug discovery, development and precision medicine.
Compound Management
Discover NCATS' compound management program, driving efficiency and innovation in drug discovery. Explore how technologies and collaborative efforts are streamlining processes and speeding the translation of research into clinical applications.
Automation
Automation supports the maintenance, operation and continuous improvement of laboratory instrumentation and processes.


