Functional Genomics Laboratory
We use powerful gene perturbation tools — such as CRISPR, RNAi and small molecule screening — to investigate how genes function, contribute to disease and can be targeted to develop better treatments.
About the Laboratory
Contact
NCATS’ Functional Genomics Laboratory (FGL), led by Ken Cheng, Ph.D., works to uncover the roles of genes in biology and disease. Our mission is to advance the field of functional genomics by using cutting-edge screening technologies to investigate gene function and regulation. We look for key genetic and molecular drivers across diseases to inform new avenues for therapy development.
To achieve this, we use a range of gene perturbation technologies — including, but not limited to, CRISPR-based genome editing, RNA interference (RNAi) and small molecule screening — to examine biological pathways at scale. These tools allow us to dissect complex gene networks and understand their roles in cell function, disease progression and therapeutic response. Our research spans multiple disease areas, leveraging high-throughput methods to generate robust, reproducible data that support both basic science and translational goals.
Our approach brings together genomics, molecular biology, computational biology and drug discovery. Combining these fields will lead to novel treatment strategies and uncover new therapeutic targets. Our goal is to share foundational insights to improve our understanding of disease mechanisms and patient care through more precise and effective therapies.
Image-based genome-wide RNAi screen for the identification and characterization of factors that regulate CENP-A expression to maintain chromosomal stability.
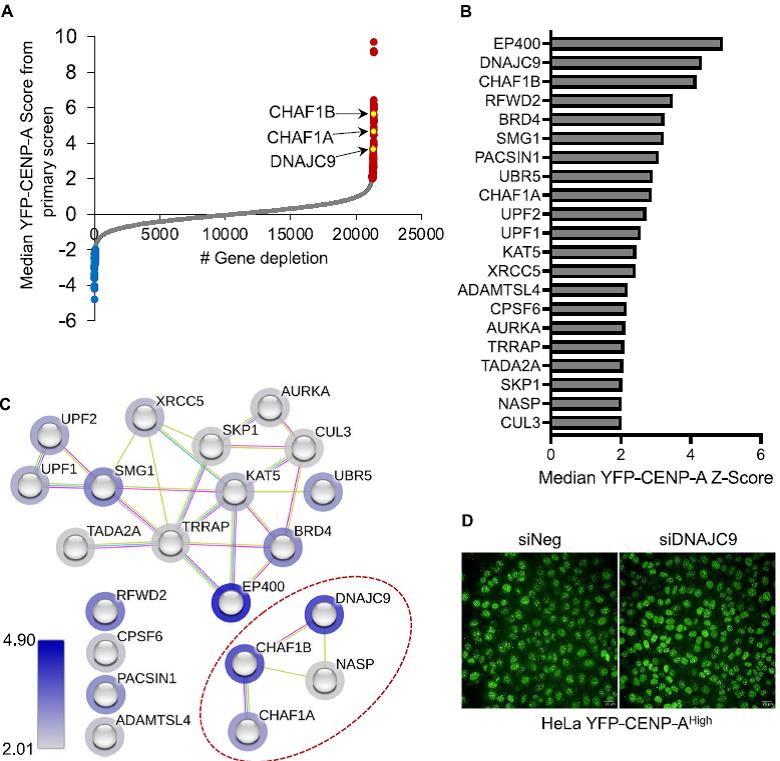
Image-based genome-wide RNAi screen for the identification and characterization of factors that regulate CENP-A expression to maintain chromosomal stability.
- Scatter plot showing median YFP-CENP-A levels (Z-score) in HeLa YFP-CENP-A High cells treated with siRNA library targeting 21,320 genes (three siRNA pergenes). Gene-level data is shown, with those that when targeted resulted in higher or lower nuclear YFP-CENP-A levels highlighted as red or blue dots, respectively.
- Bar chart showing results of primary and secondary validation screen.
- The results of STRING analysis of candidates identified in B.
- Representative images from the high-throughput primary screen.
The images were acquired at a magnification of x40 using the Opera Phenix high-content imaging system in 384-well format. Balachandra et al., EMBO J, 2024. This project was conducted in collaboration with Dr. Munira Basrai (NCI).
Image-based genome-wide RNAi screen for the identification and characterization of factors that regulate CENP-A expression to maintain chromosomal stability.

- Scatter plot showing median YFP-CENP-A levels (Z-score) in HeLa YFP-CENP-A High cells treated with siRNA library targeting 21,320 genes (three siRNA pergenes). Gene-level data is shown, with those that when targeted resulted in higher or lower nuclear YFP-CENP-A levels highlighted as red or blue dots, respectively.
- Bar chart showing results of primary and secondary validation screen.
- The results of STRING analysis of candidates identified in B.
- Representative images from the high-throughput primary screen.
The images were acquired at a magnification of x40 using the Opera Phenix high-content imaging system in 384-well format. Balachandra et al., EMBO J, 2024. This project was conducted in collaboration with Dr. Munira Basrai (NCI).
FGL News
No related news found.
FGL Publications
Browse a listing of FGL-related, peer-reviewed scientific publications that feature research supported by NCATS programs and initiatives.


